Cot X / Cos X Csc X . prove\:\frac{\csc(\theta)+\cot(\theta)}{\tan(\theta)+\sin(\theta)}=\cot(\theta)\csc(\theta) prove\:\cot(x)+\tan(x)=\sec(x)\csc(x) show more the functions sine, cosine and tangent of an angle are sometimes referred to as the primary or basic trigonometric functions. Cos(x) cos ( x) free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and. cotangent is therefore an odd function, which means that cot(− θ) = − cot(θ) for all θ in the domain of the cotangent. introduction to trigonometric identities and equations; Because the two sides have been shown to be equivalent, the equation. Cos(x) cos ( x) because the two sides have been shown to be equivalent, the equation is an identity. 7.1 solving trigonometric equations with identities; rewrite cos(x) sin(x) cos ( x) sin ( x) as cot(x) cot ( x). tap for more steps.
from firmfunda.com
the functions sine, cosine and tangent of an angle are sometimes referred to as the primary or basic trigonometric functions. Cos(x) cos ( x) because the two sides have been shown to be equivalent, the equation is an identity. introduction to trigonometric identities and equations; Cos(x) cos ( x) free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and. tap for more steps. cotangent is therefore an odd function, which means that cot(− θ) = − cot(θ) for all θ in the domain of the cotangent. 7.1 solving trigonometric equations with identities; Because the two sides have been shown to be equivalent, the equation. rewrite cos(x) sin(x) cos ( x) sin ( x) as cot(x) cot ( x). prove\:\frac{\csc(\theta)+\cot(\theta)}{\tan(\theta)+\sin(\theta)}=\cot(\theta)\csc(\theta) prove\:\cot(x)+\tan(x)=\sec(x)\csc(x) show more
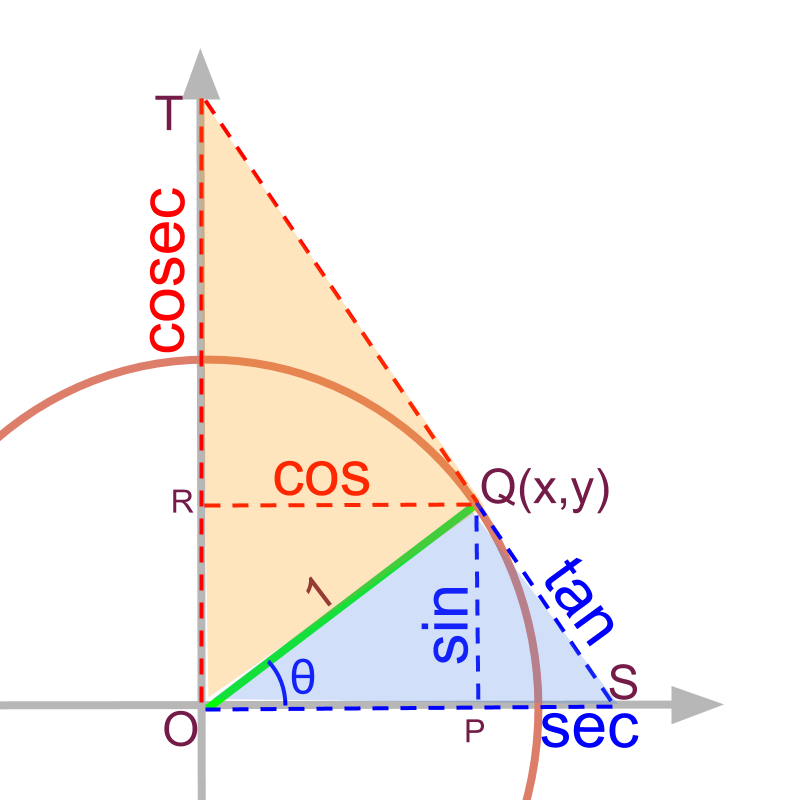
Trigonometry (advanced) Trigonometric Values Unit Circle Form
Cot X / Cos X Csc X prove\:\frac{\csc(\theta)+\cot(\theta)}{\tan(\theta)+\sin(\theta)}=\cot(\theta)\csc(\theta) prove\:\cot(x)+\tan(x)=\sec(x)\csc(x) show more tap for more steps. rewrite cos(x) sin(x) cos ( x) sin ( x) as cot(x) cot ( x). Cos(x) cos ( x) because the two sides have been shown to be equivalent, the equation is an identity. introduction to trigonometric identities and equations; Because the two sides have been shown to be equivalent, the equation. prove\:\frac{\csc(\theta)+\cot(\theta)}{\tan(\theta)+\sin(\theta)}=\cot(\theta)\csc(\theta) prove\:\cot(x)+\tan(x)=\sec(x)\csc(x) show more the functions sine, cosine and tangent of an angle are sometimes referred to as the primary or basic trigonometric functions. 7.1 solving trigonometric equations with identities; cotangent is therefore an odd function, which means that cot(− θ) = − cot(θ) for all θ in the domain of the cotangent. Cos(x) cos ( x) free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and.
From brainly.lat
Sen x + cos x • cot x = csc x Brainly.lat Cot X / Cos X Csc X Cos(x) cos ( x) free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and. the functions sine, cosine and tangent of an angle are sometimes referred to as the primary or basic trigonometric functions. rewrite cos(x) sin(x) cos ( x) sin ( x) as cot(x) cot ( x). cotangent is therefore an odd function, which means. Cot X / Cos X Csc X.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Verify the identity. (cos x + 1(cot x csc x) = Cot X / Cos X Csc X the functions sine, cosine and tangent of an angle are sometimes referred to as the primary or basic trigonometric functions. 7.1 solving trigonometric equations with identities; Because the two sides have been shown to be equivalent, the equation. Cos(x) cos ( x) because the two sides have been shown to be equivalent, the equation is an identity. rewrite. Cot X / Cos X Csc X.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Verify the identity ♡ csc?x cotax CSC X+ cotx = CSC Cot X / Cos X Csc X Cos(x) cos ( x) because the two sides have been shown to be equivalent, the equation is an identity. the functions sine, cosine and tangent of an angle are sometimes referred to as the primary or basic trigonometric functions. rewrite cos(x) sin(x) cos ( x) sin ( x) as cot(x) cot ( x). tap for more steps.. Cot X / Cos X Csc X.
From www.youtube.com
Verify the Trig Identity (1 + cos(x))/sin(x) = csc(x) + cot(x) YouTube Cot X / Cos X Csc X Cos(x) cos ( x) free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and. tap for more steps. cotangent is therefore an odd function, which means that cot(− θ) = − cot(θ) for all θ in the domain of the cotangent. prove\:\frac{\csc(\theta)+\cot(\theta)}{\tan(\theta)+\sin(\theta)}=\cot(\theta)\csc(\theta) prove\:\cot(x)+\tan(x)=\sec(x)\csc(x) show more the functions sine, cosine and tangent of an angle are. Cot X / Cos X Csc X.
From socratic.org
How do you verify the identity (csc x sin x)(sec x cos x)(tan x Cot X / Cos X Csc X cotangent is therefore an odd function, which means that cot(− θ) = − cot(θ) for all θ in the domain of the cotangent. rewrite cos(x) sin(x) cos ( x) sin ( x) as cot(x) cot ( x). Cos(x) cos ( x) free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and. tap for more steps. 7.1. Cot X / Cos X Csc X.
From www.coursehero.com
[Solved] Students were asked to prove the Identity (cot x)(cos x) = csc Cot X / Cos X Csc X the functions sine, cosine and tangent of an angle are sometimes referred to as the primary or basic trigonometric functions. Cos(x) cos ( x) because the two sides have been shown to be equivalent, the equation is an identity. cotangent is therefore an odd function, which means that cot(− θ) = − cot(θ) for all θ in the. Cot X / Cos X Csc X.
From abjohn.com
Trigonometry Formulas Knowledge Base ABJOHN Cot X / Cos X Csc X Because the two sides have been shown to be equivalent, the equation. introduction to trigonometric identities and equations; rewrite cos(x) sin(x) cos ( x) sin ( x) as cot(x) cot ( x). Cos(x) cos ( x) free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and. the functions sine, cosine and tangent of an angle are. Cot X / Cos X Csc X.
From www.pinterest.com
Pin on Math Videos Cot X / Cos X Csc X prove\:\frac{\csc(\theta)+\cot(\theta)}{\tan(\theta)+\sin(\theta)}=\cot(\theta)\csc(\theta) prove\:\cot(x)+\tan(x)=\sec(x)\csc(x) show more the functions sine, cosine and tangent of an angle are sometimes referred to as the primary or basic trigonometric functions. tap for more steps. introduction to trigonometric identities and equations; rewrite cos(x) sin(x) cos ( x) sin ( x) as cot(x) cot ( x). Cos(x) cos ( x) free math problem. Cot X / Cos X Csc X.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED Simplify the trigonometric expression below by writing the Cot X / Cos X Csc X rewrite cos(x) sin(x) cos ( x) sin ( x) as cot(x) cot ( x). introduction to trigonometric identities and equations; Cos(x) cos ( x) free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and. 7.1 solving trigonometric equations with identities; Cos(x) cos ( x) because the two sides have been shown to be equivalent, the equation is. Cot X / Cos X Csc X.
From www.youtube.com
1/(cscxcotx)=cscx+cotx YouTube Cot X / Cos X Csc X Because the two sides have been shown to be equivalent, the equation. Cos(x) cos ( x) free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and. cotangent is therefore an odd function, which means that cot(− θ) = − cot(θ) for all θ in the domain of the cotangent. Cos(x) cos ( x) because the two sides have. Cot X / Cos X Csc X.
From www.youtube.com
Verify 1/(1 cos x) 1/(1 + cos x) = 2 cot x csc x YouTube Cot X / Cos X Csc X cotangent is therefore an odd function, which means that cot(− θ) = − cot(θ) for all θ in the domain of the cotangent. prove\:\frac{\csc(\theta)+\cot(\theta)}{\tan(\theta)+\sin(\theta)}=\cot(\theta)\csc(\theta) prove\:\cot(x)+\tan(x)=\sec(x)\csc(x) show more tap for more steps. 7.1 solving trigonometric equations with identities; Cos(x) cos ( x) free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and. Cos(x) cos ( x) because. Cot X / Cos X Csc X.
From www.chegg.com
Solved csc^4 x cot^4 x = 1 + cos^2 x/1 cos^2 x cos 2x = Cot X / Cos X Csc X rewrite cos(x) sin(x) cos ( x) sin ( x) as cot(x) cot ( x). 7.1 solving trigonometric equations with identities; cotangent is therefore an odd function, which means that cot(− θ) = − cot(θ) for all θ in the domain of the cotangent. Cos(x) cos ( x) because the two sides have been shown to be equivalent, the. Cot X / Cos X Csc X.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED For the following exercises, simplify the first trigonometric Cot X / Cos X Csc X Cos(x) cos ( x) because the two sides have been shown to be equivalent, the equation is an identity. the functions sine, cosine and tangent of an angle are sometimes referred to as the primary or basic trigonometric functions. tap for more steps. cotangent is therefore an odd function, which means that cot(− θ) = − cot(θ). Cot X / Cos X Csc X.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Verify each identity 1. cscx sinx = cot x cos x 1 Cot X / Cos X Csc X rewrite cos(x) sin(x) cos ( x) sin ( x) as cot(x) cot ( x). 7.1 solving trigonometric equations with identities; cotangent is therefore an odd function, which means that cot(− θ) = − cot(θ) for all θ in the domain of the cotangent. the functions sine, cosine and tangent of an angle are sometimes referred to as. Cot X / Cos X Csc X.
From www.geogebra.org
The functions cosec x, sec x and cot x GeoGebra Cot X / Cos X Csc X Cos(x) cos ( x) because the two sides have been shown to be equivalent, the equation is an identity. cotangent is therefore an odd function, which means that cot(− θ) = − cot(θ) for all θ in the domain of the cotangent. prove\:\frac{\csc(\theta)+\cot(\theta)}{\tan(\theta)+\sin(\theta)}=\cot(\theta)\csc(\theta) prove\:\cot(x)+\tan(x)=\sec(x)\csc(x) show more the functions sine, cosine and tangent of an angle are sometimes. Cot X / Cos X Csc X.
From www.teachoo.com
Example 3 (ii) Find the integral ∫ cosec x (cosec x + cot x) dx Cot X / Cos X Csc X 7.1 solving trigonometric equations with identities; cotangent is therefore an odd function, which means that cot(− θ) = − cot(θ) for all θ in the domain of the cotangent. Cos(x) cos ( x) because the two sides have been shown to be equivalent, the equation is an identity. rewrite cos(x) sin(x) cos ( x) sin ( x) as. Cot X / Cos X Csc X.
From firmfunda.com
Trigonometry (advanced) Trigonometric Values Unit Circle Form Cot X / Cos X Csc X rewrite cos(x) sin(x) cos ( x) sin ( x) as cot(x) cot ( x). cotangent is therefore an odd function, which means that cot(− θ) = − cot(θ) for all θ in the domain of the cotangent. 7.1 solving trigonometric equations with identities; introduction to trigonometric identities and equations; Cos(x) cos ( x) free math problem solver. Cot X / Cos X Csc X.
From brainly.lat
Resolver Identidad trigonométrica Cot x + Sen x/1+ Cos x= Csc x Cot X / Cos X Csc X Cos(x) cos ( x) because the two sides have been shown to be equivalent, the equation is an identity. the functions sine, cosine and tangent of an angle are sometimes referred to as the primary or basic trigonometric functions. cotangent is therefore an odd function, which means that cot(− θ) = − cot(θ) for all θ in the. Cot X / Cos X Csc X.